The differences and characteristics between TPEE and TPE.
Release time:
2019-12-12
First of all, TPE has a meaning that refers to all thermoplastic elastomers, including TPR, TPU, TPV, TPEE, TPO, TPAE, etc. The full name in Chinese is Thermo-Plastic Elastomer. Due to historical and usage habits, there is currently no unified naming for thermoplastic elastomers both domestically and internationally. In most regions, it is customary to refer to thermoplastic elastomers collectively as TPE in English abbreviation. Another interpretation is that TPE is a general term for thermoplastic elastomers, TPU is thermoplastic polyurethane, TPV is vulcanized thermoplastic elastomer, and TPR is commonly understood in China as thermoplastic rubber, with SBS as the base material.
Differences and characteristics of TPEE and TPE
Many customers often ask about the differences between TPEE and TPE when inquiring about TPEE materials.
First, TPE refers to all thermoplastic elastomers, including TPR, TPU, TPV, TPEE, TPO, TPAE, etc. The full Chinese name is Thermo-Plastic Elastomer. Due to historical and usage habits, there is currently no unified naming for thermoplastic elastomers domestically and internationally, and most regions habitually refer to thermoplastic elastomers collectively as TPE. Another explanation is that TPE is a general term for thermoplastic elastomers, TPU is thermoplastic polyurethane, TPV is vulcanized thermoplastic elastomer, and TPR is generally considered thermoplastic rubber in China, based on SBS.
TPE characteristics: It has high elasticity, high strength, and high resilience like rubber, while also possessing characteristics suitable for injection molding. It is environmentally friendly, non-toxic, and safe, with a wide hardness range, excellent coloring properties, a soft touch, weather resistance, fatigue resistance, and temperature resistance. Its processing performance is superior, does not require vulcanization, can be recycled to reduce costs, can be re-injected molded, and can bond with base materials like PP, PE, PC, PS, ABS, or be molded independently.
TPEE (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer) is a block copolymer containing polyester hard segments and polyether soft segments.
TPEE characteristics: It has the elasticity of rubber and the strength of engineering plastics; the soft segments give it elasticity similar to rubber; the hard segments provide it with processing performance, making it like plastic. Compared to rubber, it has better processing performance and a longer service life; compared to engineering materials, it also has high strength, while its flexibility and dynamic mechanical properties are better. The hardness of TPEE can range from Shore 30 to 82D, with its elasticity and strength lying between rubber and plastic.
TPEE is mainly used in fields that require shock absorption, impact resistance, flexibility, sealing, elasticity, oil resistance, chemical resistance, and sufficient strength. For example: polymer modification, automotive parts, high-speed rail gaskets, high and low temperature resistant wire sheaths, hydraulic hoses, shoe materials, drive belts, rotationally molded tires, flexible couplings, soundproof gears, elevator guide rails, and corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant materials for chemical equipment pipeline valves.
Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer (TPEE) is an engineering plastic material developed by CCP over many years with significant investment in human and material resources, produced with CCP's proprietary technology to supply the industry with the best quality TPEE at lower costs. Since 2017, all production capacity has been contracted to DuPont for OEM branding, marketed externally as DuPont Bexloy.
TPEE (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer) is known in Chinese as 热塑性聚酯弹性体, and its chemical formula can be represented as follows:
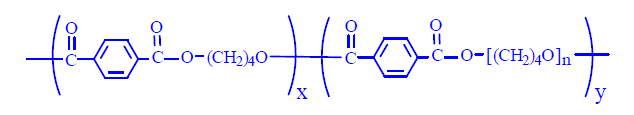
It is formed by the copolymerization of 1,4-butanediol and polytetramethylene glycol with dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) or terephthalic acid (PTA), and can be made into thermoplastic polyester elastomer composites through mixing processes. TPEE has many excellent properties and is widely used in electrical, telecommunications, and automotive industries.
Characteristics of TPEE
◆Excellent heat resistance, with a Vicat softening point of 120-200℃, the best heat resistance among TPEs.
◆Excellent low-temperature flexibility, can withstand cold down to -54℃.
◆Good mechanical strength, strong and tough properties.
◆Excellent bending fatigue resistance.
◆Rapid crystallization, easy to mold.
◆Excellent oil and chemical resistance.
◆Low water absorption, excellent dimensional stability.
◆Low friction coefficient, wear-resistant.

If there is any infringement in the above materials, please contact the administrator for timely deletion.
Tag:
Previous Page
Recommend News
2018-04-09
Share

